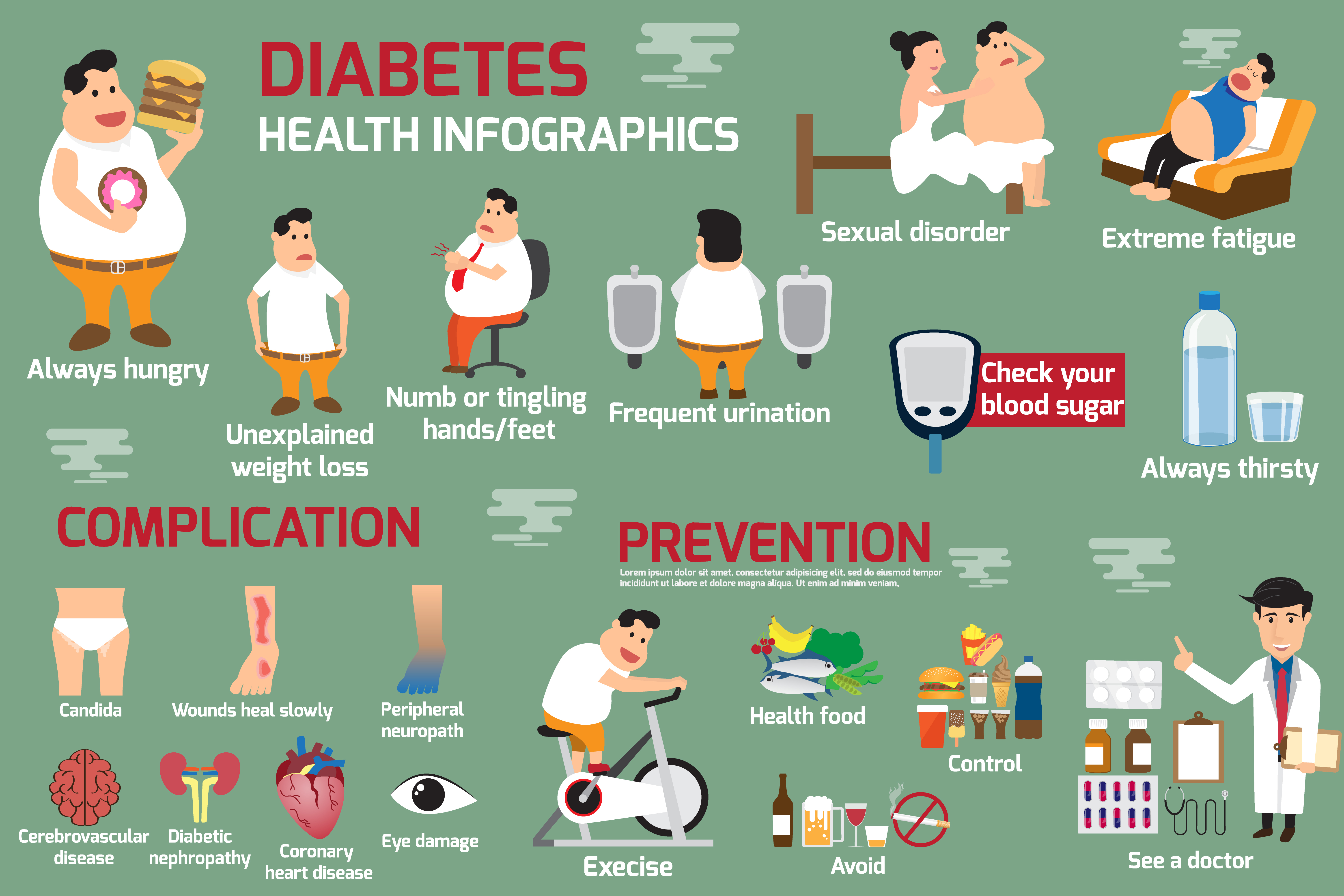
Definition of DM
DM is a group of diseases characterized by hyperglycemia (elevated blood glucose) resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both.
Diagnostic criteria for DM
- Symptoms include: Thirst, increased daily urine amount, weight loss, and causal plasma glucose greater than 200 mg/ dL
- With empty stomach more than 8 hours, the plasma glucose level exceeds 126 mg/dL
- 2 hours after taking the 75-g oral glucose test, the plasma glucose level exceeds 200 mg/ dL.
Note: when any aforementioned symptom is fulfilled, it is deemed diabetes mellitus.
- Glycated A1c (HbA1c) ≥ 6.5%.
In the absence of unequivocal hyperglycemia, diagnosis requires two abnormal test results obtained at the same time or at two different time points.
DM Classification
- Type 1 DM : pancreatic β cell destruction and insulin deficiency.
- Type 2 DM : insulin resistance.
- Other specific types: resulting from pancreatitis, endocrine disorders, or drug
- Gestational DM : hyperglycemia with first recognition during pregnancy.
Acute complications of DM
- Hypoglycemia: Low level glucose is induced by medication overdose, insufficient food intake, or excessive work-out.
- Ketpacidosis: excessive ketone accumulation in the body results distinct gastrointestinal symptoms and acute short breath.
- Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome: extremely high hyperglycemia with combination of dehydration and consciousness disturbance.
Chronic complications of DM
- Retinopathy : vision blurring or loss of vision.
- Neuropathy : numbed and painful limbs, postural dizziness, constipation or diarrhea, and impotence.
- Nephropathy : protein in urine, edema, hypertension, and renal failure.
- Cardiovascular disease : atherosclerosis incurs stoke, myocardial infarction, lower limb circulation disturbance.
- Foot ailment : ulceration, necrosis, gangrene, infection, and amputation.
DM Treatment
- Diet : adequate calories and balanced nutrients.
- Exercise : 30-minute to an hour daily exercise with moderate intensity.
- Drugs : oral medication or insulin injection.
- Comprehensive health education.
- Regular and normal life style.
Goals for DM control
- Plasma glucose before mea l : 70 - 130 mg/dL.
- Plasma glucose after meal : less than 180 mg/dL.
- HbA1c : lower than 7.0 %.