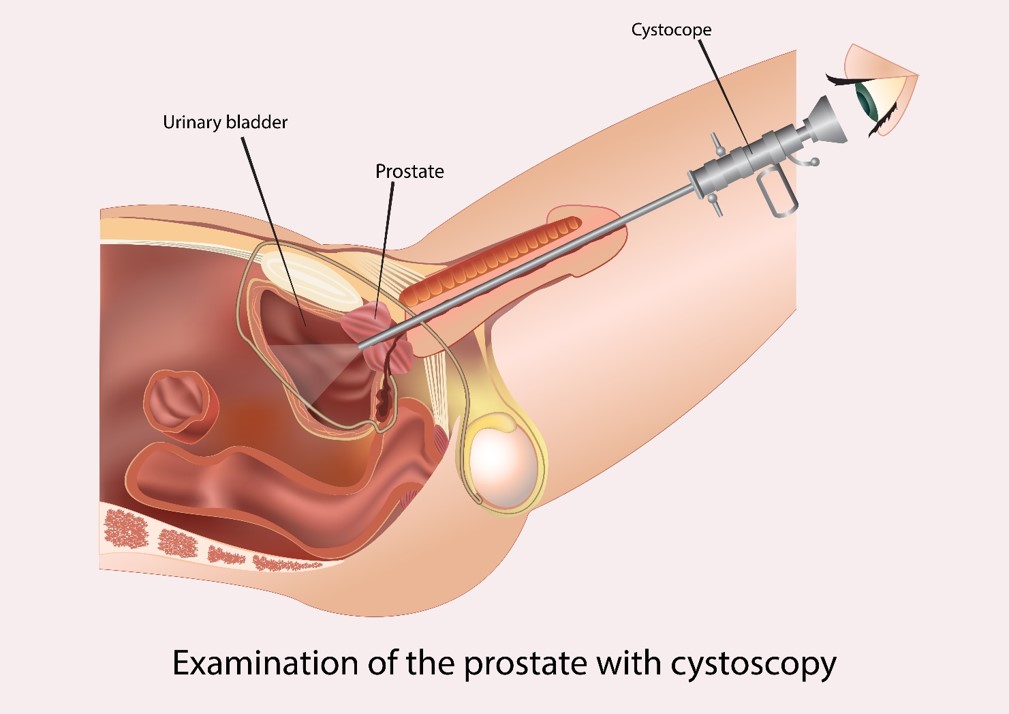
Purpose of Examination
- Observe for any lesion or abnormal anatomy of the bladder, urethra and ureteral orifice.
- Dissect some tissue and biopsy to examine closely.
- Small stones from seniors sometimes can be removed.
Pre-Examination Procedures
- Fill out the Agreement of Examination.
- Drink more water before examination to increase urination during examination.
- Follow physician advice before examination to give local anesthesia perfusion.
Examination Procedures
- Keep the body still during examination to avoid injuring the urinary tract.
- The examination is usually implemented through lithotomy position (lying flat with legs elevated).
- The patient can take deep breath and relax the whole body to reduce the discomfort experienced during the examination with the still position.
Post-Examination Procedures
- The patient may experience increase number of urination, pain during urination, bleeding, and bladder or kidney pain.
- Take painkiller, hot compress or bathing in lukewarm water to relieve pain when necessary.
- Pink urine is normal but in case of consistently bloody-red urine or blood clots, notify the nurse immediately.
- In case of difficulty with urination that leads to urinary retention or fever, seek for help from ER or outpatient.
- Drink water after the examination to promote urine and contrast media discharge.