Introduction
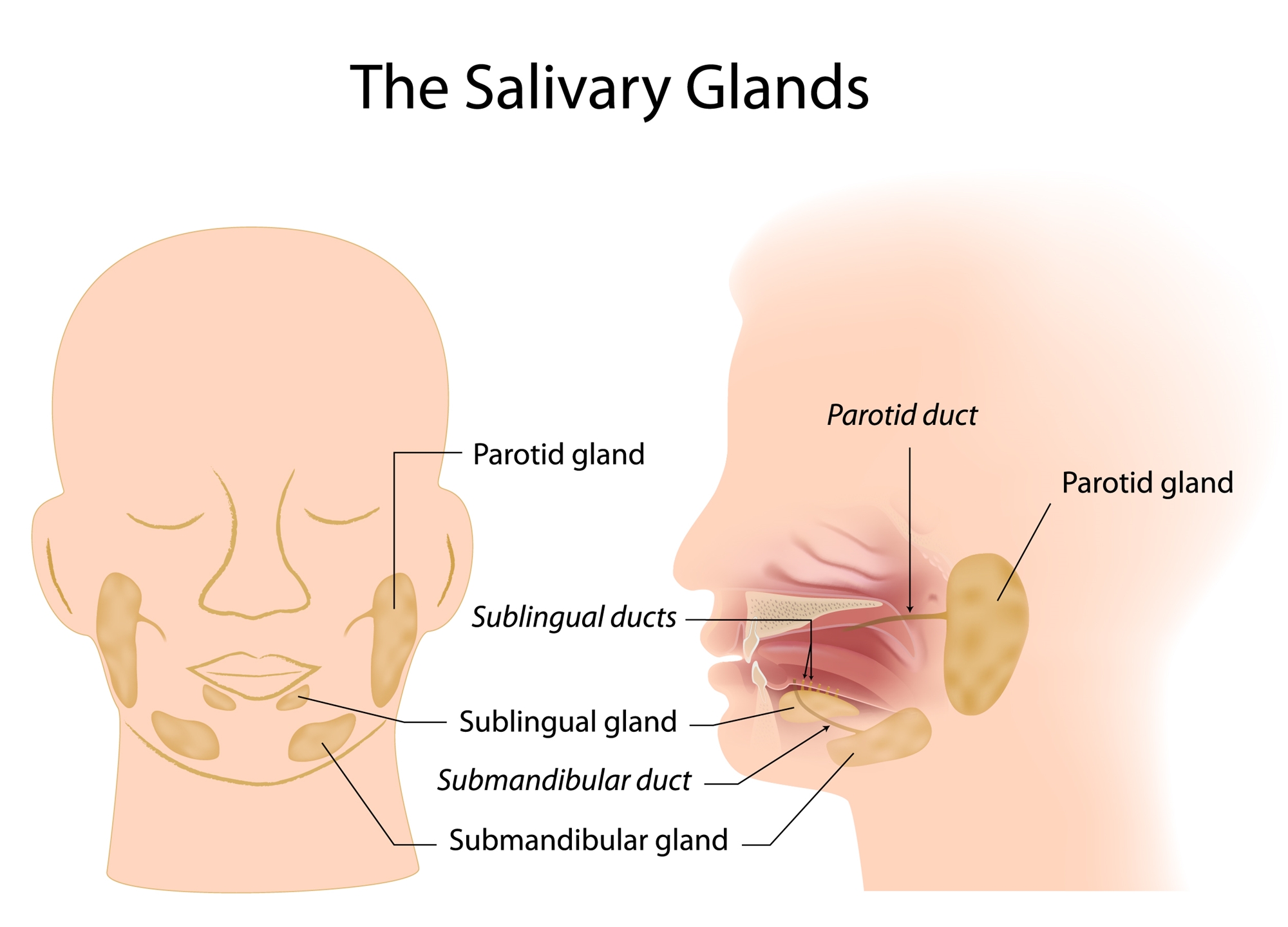
Human’s salivary glands include parotid glands, submandibular glands, sublingual glands and minor salivary glands. The parotid gland is the largest salivary gland in human, located at anterior and inferior to ear. What should be noted is that facial nerve controlling facial muscles movement goes through it. So when some parotid gland diseases invade facial nerve, patients will have facial palsy. Both sublingual glands and submandibular glands are located at medial side of mandible with sublingual glands in the front and submandibular glands in the back. Those salivary glands will secret saliva into oral cavity through individual salivary duct. Besides, there are many minor salivary glands located under oral mucosa.
Our daily saliva secretion is about 1500 to 2000CC. The saliva is composed of water, many electrolytes, proteins, and transudation. The pH value of saliva is between 6 to 7.
Saliva has functions as follows:
- Digestion: Saliva can rinse food, making food easy to swallow. Also, saliva contains digestive enzyme and hydrolyzing amylum in the food.
- Secretion: According to experiments, electrolytes, drugs, and viruses in serum can be released into saliva.
- Anti-microorganism: Special enzyme and immunoglobulin in saliva have specific or non-specific antibacterial functions.
- Protecting teeth and mucosa: Saliva has buffering effect to stabilize pH value in the mouth and protect enamel to prevent decayed teeth. Also, mucins in saliva have protecting teeth and mucosa.
Common salivary gland diseases
Infectious salivary gland diseases
- Virus parotiditis: What is called mumps is the most common infectious parotid gland disease. The main symptoms are acute painful swelling in unilateral or bilateral parotid glands. Patients recover in 5-7 days spontaneously, symptomatic treatment needed only.
- What should be noted is that pediatric parotiditis might complicate aseptic encephalopathy. Parotiditis in adult might cause hearing loss or orchitis, which might lead to infertility. Some other diseases have similar symptoms like parotiditis. For example, neck lymphoadenopathy and suppurative parotiditis are caused by bacterial infection, antibiotic treatment needed.
- Acute suppurative parotiditis: We can find pus gush out from orifice of parotid duct in mouth by squeezing swelling parotid gland to make diagnosis. The main treatments are oral or intravenous antibiotics.
- Sjogren's syndrome: A chronic, slow progression autoimmune disease. Its classical clinical symptoms include dry eyes keratoconjunctivitis and xerostomia. Ways to examine xerostomia are saliva flow rate test and sialoscintigraphy; lower lip salivary gland biopsy can make sure diagnosis. Besides, xerostomia is common in head and neck cancer patients who receive radiotherapy. Xerostomia causes disturbances of talking and eating; we can only offer symptomatic treatment and water supplement.
- Sialolithiasis: Most sialolithiasis occur in submandibular glands. The classical symptoms of sialolithiasis are submandibular area progressive swelling especially after eating sour food. The swelling will recover after local massage. Low intake of water or bacterium multiplication in mouth might form stone. If salivary duct is blocked by stone, the block makes salivary gland infected and lead to painful swelling whenever eating. Way to treat sialolithiasis of submandibular gland is lithotripsy via mouth. If the stone is located in salivary gland or if chronic sialoadenitis happens, excision of salivary gland should be considered.
Salivary gland tumor
About 80% of salivary gland tumors happen in parotid glands. 80% parotid gland tumors are benign, among which pleomorphic adenoma (mixed tumor) is the most common, followed by Warthin's tumor. The later seems to increase gradually in recent years, which may be related to smoking. 50% submandibular gland tumors are malignant. 80% of sublingual gland tumors and minor salivary gland tumors are malignant except for common mucocele.
Ways to distinguish benign or malignant tumors are mainly fine needle aspiration, and image study(CT scan or MRI).Treatment principle of parotid gland tumor is surgery whether benign or malignant.
Submandibular gland tumors often show painless mass. Clinical symptom of sublingual gland tumors and minor salivary gland tumors is hard mass in mouth. Because the rate of malignant tumors is higher than that of parotid gland, treatment principle is surgery. If post-operative pathologic report reveals high grade malignancy or neck lymph node metastasis, post-operative radiotherapy is recommended to increase local control rate. Adjuvant chemotherapy does not have enough clinical evidence to support significant effect.

