Urinary tract infection refers to infection of any tissue or organ in the urinary system, including kidney, ureter, bladder, and urethra infections, which can all be called urinary tract infections.
Symptom
- The most common symptoms of infants are fever, decreased appetite, poor spirits, irritable crying, and even vomiting, jaundice and so on.
- Older children may have symptoms such as urination pain, frequent urination, urgency, burning sensation when voiding, nocturia, hematuria, lower abdominal pain, urinary incontinence, fever and flank pain.
Diagnostic check
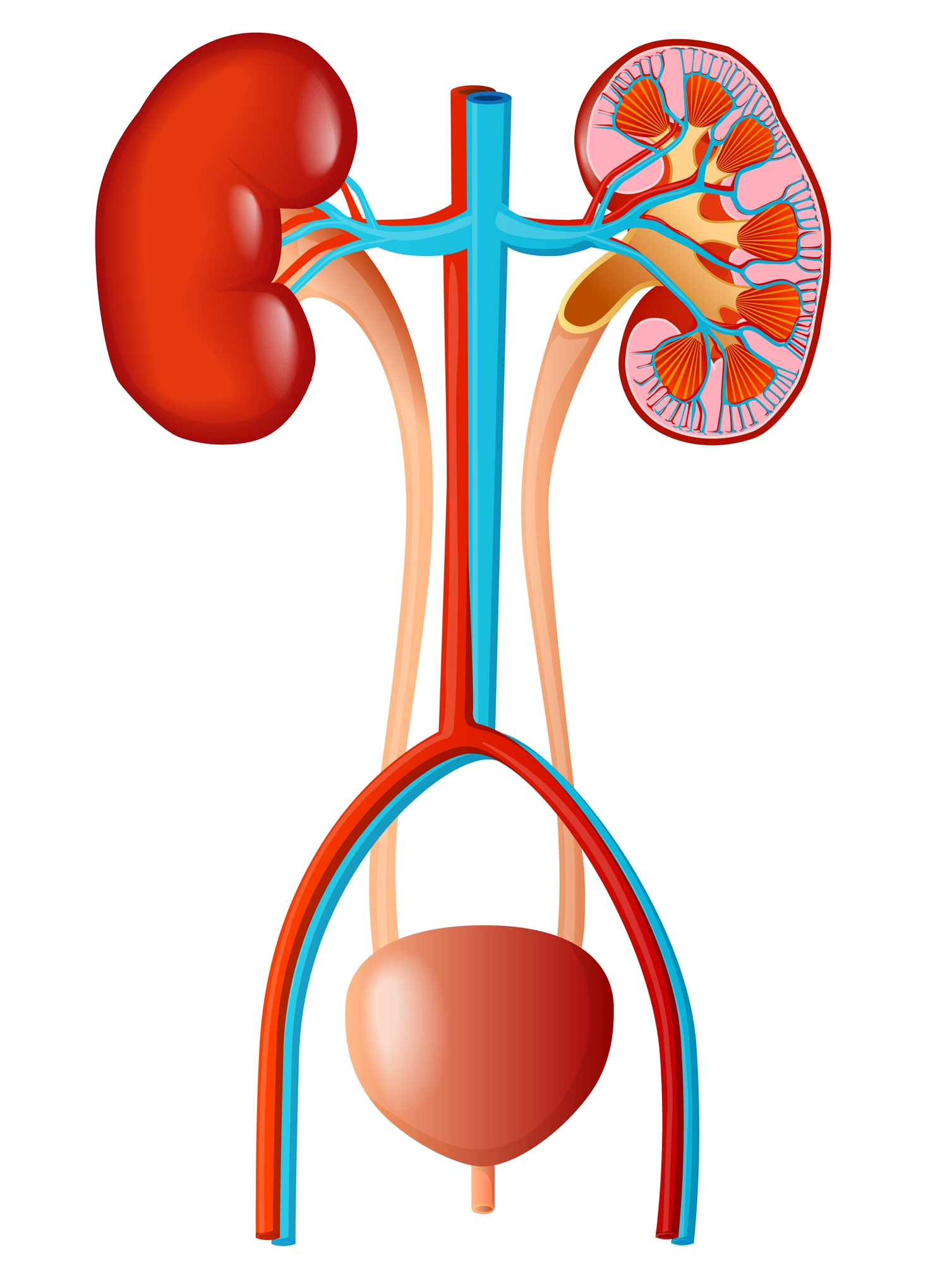
- Urine examination and bacterial culture:
Check whether there are infections and types of bacteria in the urine. - Kidney ultrasound examination:
Check for structural abnormalities, dilation of the renal pelvis, or nephritis. - Voiding cystoureterography (VCUG): To check whether there is urine reflux into the ureter, kidney, or urethral malformation.
- Nuclear renal scan (DMSA): To
check whether the kidney cortex has scars formation due to urinary tract infection
Treatment
- For infants and young children with febrile urinary tract infections, it is recommended to be hospitalized to receive intravenous antibiotics treatment because they are worried about the complications of sepsis. The treatment periods varies from 7 to 21 days (including intravenous and oral antibiotic treatment) depending on its severity.
- However, older children and adolescents who have no systemic symptoms can receive oral antibiotics in the outpatient clinic. If a potential congenital urinary tract abnormality is detected, prophylactic antibiotic treatment or surgical treatment is considered according to its severity.
Precautions for home care
- Diapers should be changed frequently to reduce the chance of urinary tract infection.
- Toddlers or children in childhood should avoid the opportunity for them to hold back urine.
- Girls should pay attention to keeping the perineum clean. When cleaning, clean the urethral opening to the anus (wipe from top to bottom or from front to back) to reduce the chance of retrograde infection.
- Boys should pay attention to the cleanliness of the foreskin to avoid bacterial infection.
- The best way to take a bath is to take a shower. If you have to take a sitting bath, it is not advisable to soak for too long.
- When a child has a fever of unknown origin, he must see a doctor, be sure to receive antibiotic treatment according to the doctor's prescription, and never stop the medicine by himself.
- Congenital abnormalities of the urinary tract system should be followed up regularly.

