Scabies is a contagious skin infestation by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. The adult Sarcoptes scabiei, about 0.3mm in size, is a mite parasitic in the cuticle of human skin, during which it digs subcutaneous tunnels and leaves eggs and feces, which causes skin allergies and itching symptoms.
The infection route of scabies is contact infection, which often occurs in hospital, school, army, nursing home, prison and other social environment, or in duty rooms and hotels which are not thoroughly cleaned and disinfected.
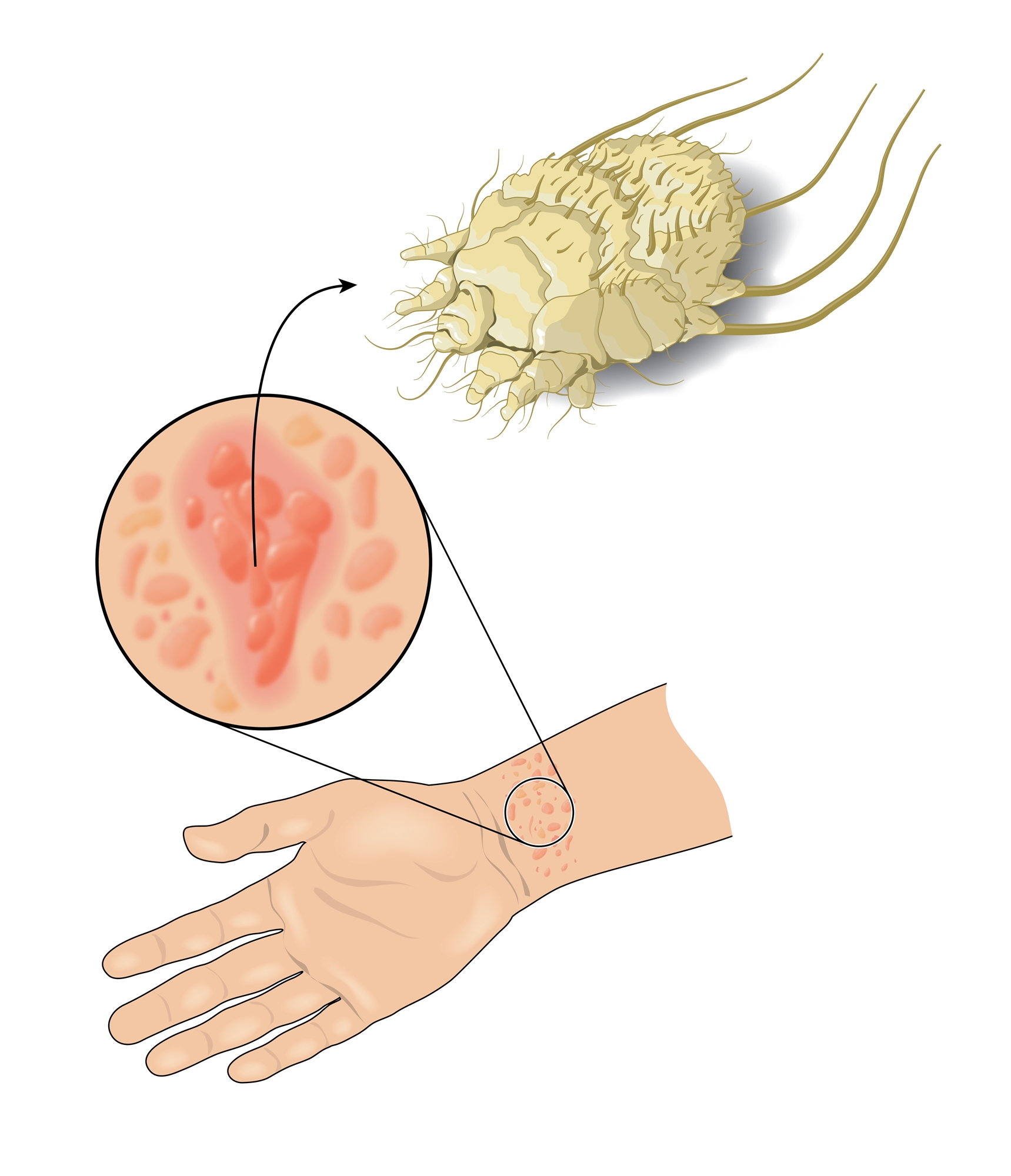
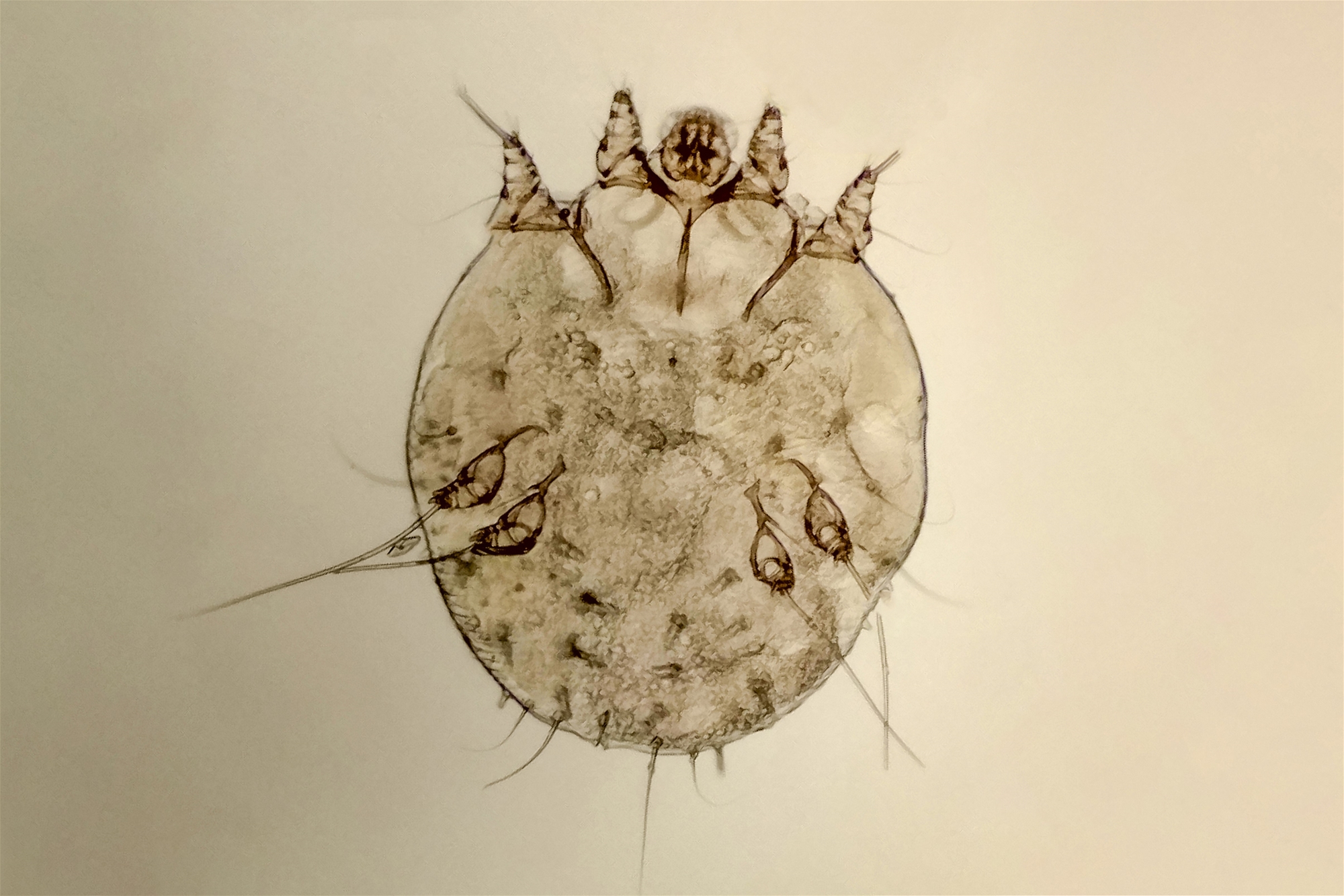
Notes for Scabies Treatment
- Adults: After taking a shower, use up Permethrin ointment at one go and apply it all over the body from below the neck to the sole of the foot, including fingertips, armpits and vulva (whether there are lesions or not). Avoid the mucous membrane of the body when applying, and wash off the ointment after 8-12 hours. Only apply it once a week for two weeks.
- Children: Apply Permethrin ointment all over the body, including the head and face, as well as fingertips, armpits and vulva (whether there are lesions or not). Avoid the mucous membrane of the body when applying, and wash off the ointment after 8-12 hours.
- Sterilize close-fitting clothes, underwear, bed sheets and pillowcases with hot water (above 60℃) for at least 15 minutes. When hot water is not available, use a dryer to sterilize your laundry at 60℃ for 15 minutes.
- Clothes that cannot be heated and disinfected should be wrapped in plastic bags for 2 weeks before wearing. Dry mattresses, straw mattresses, etc. under sun.
- Please vacuum the furniture and floors to remove any scurf and disinfect them with diluted bleach (ratio 1:100).
- It is suggested that family members living together should be treated at the same time to avoid cross infection.
- After the cure of scabies, allergic reaction and itching may continue for weeks to months. Please proceed with follow up treatment in the dermatology department.

