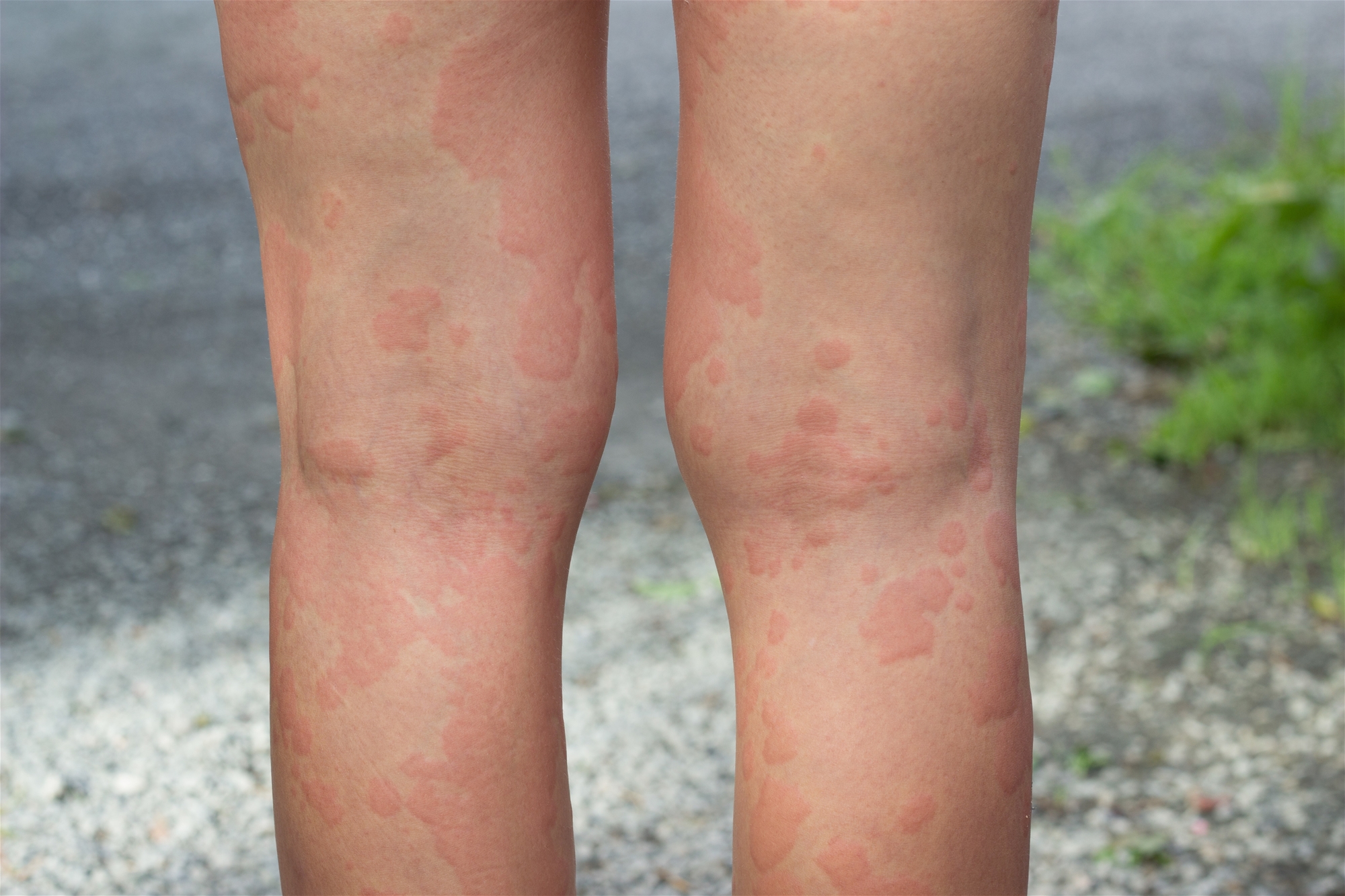
Urticaria, commonly known as wheals, is a common skin disorder. Symptoms are temporary, itchy, raised bumps that usually clear up in a few hours, but may return later to other parts of the body. In addition to the common skin symptoms, severe cases are combined with systemic symptoms, such as joint swelling and pain, lip and eyelid swelling (vascular edema), abdominal pain, dyspnea, and even anaphylactic shock, so it is not advisable to take it lightly.
Urticaria is generally classified as acute and chronic. Acute urticaria can be traced to the cause, and the condition gradually improves within hours to weeks. Food and medicine are the most common causes of hives. It is diagnosed as chronic urticaria if the recurrence of wheals lasts more than 6 weeks. It is usually impossible to find a specific allergen. Therefore, patient cooperation with the physician can generally achieve a good therapeutic effect. Otherwise, even visiting famous doctors is in vain.
The following three points should be paid attention to in terms of treatment:
- Prevention is better than cure. Be aware of your allergies to certain foods, drugs or physical factors and avoid them.
- Antihistamine is a first-line drug in the treatment of urticaria at present. Some antihistamines have somnolence effect. Therefore, if your work requires you to stay focused like drivers, you should inform your doctor beforehand.
- Patience is required in the treatment of chronic urticaria. The treatment time usually takes months. The important thing is not to seek medicines everywhere, but to see a doctor on a regular basis and adjust the use of medication.

