What is a tracheostomy?
A tracheostomy, commonly known as a “trach,” is a medical procedure that creates a small opening at the front of the neck, inserting a tracheostomy tube into the trachea to allow air to move easily in and out of the lungs.
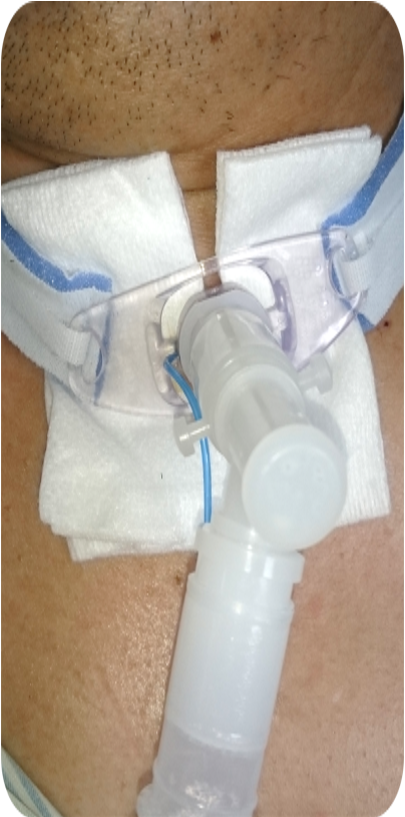

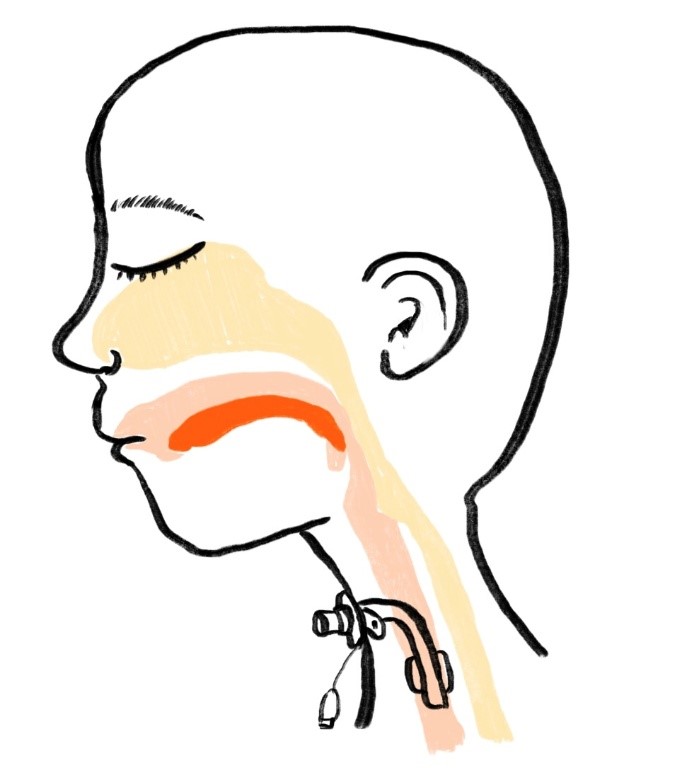
Indications for tracheostomy
- Respiratory failure requiring prolonged ventilator use (>1–2 weeks)
- Upper airway obstruction due to tumor, infection, foreign body, or trauma
- Long-term airway protection required due to impaired consciousness, swallowing difficulty, stroke, or neuromuscular disease.
Timing of tracheostomy
- Tracheostomy can reduce airway injury caused by prolonged intubation and improve comfort. The medical team evaluates duration of ventilation, airway obstruction risk, and cough function.
Complications of tracheostomy
- Short-term complications: bleeding, infection, pneumothorax, subcutaneous emphysema, tube malposition, accidental decannulation.
- Long-term complications: stomal stenosis, granulation tissue, tracheal stenosis, voice changes, long-term tube dependence.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advantages: Tracheostomy can help you breathe more easily and comfortably, reduce damage to the vocal cords, and make speech and swallowing training easier. It also helps lower the risk of pneumonia.
- Disadvantages: The tube needs to be replaced regularly. You may have some difficulty speaking, and there is a risk of secretion buildup or infection. The appearance of the neck may also change.

