Acute otitis media is defined as acute inflammation of the middle ear within three weeks. Common acute symptoms include earache, fever, general fatigue and hearing loss.
Eustachian tube blockage due to tissue edema is the most likely cause of acute otitis media. The most common cause of acute otitis media is upper respiratory tract infection. The source of infection is usually viruses or bacteria, but allergic reactions or other inflammatory reactions can also cause similar symptoms in the eustachian tube.
The most common bacteria in acute otitis media are streptococcus pneumoniae, haemophilus, type A streptococcus and staphylococcus aureus. On the other hand, the most common respiratory viruses include respiratory syncytial virus, influenza virus, enterovirus and rhinovirus.
Symptoms
When the middle ear is acutely infected with bacteria, the pressure in the middle ear cavity increases sharply, causing pain. Sometimes the middle ear cavity can be purulent and swollen, and the eardrum will burst and ooze pus before treatment. Hearing impairment may occur when there is too much empyema for a prolonged period of time in the middle ear to be treated properly.
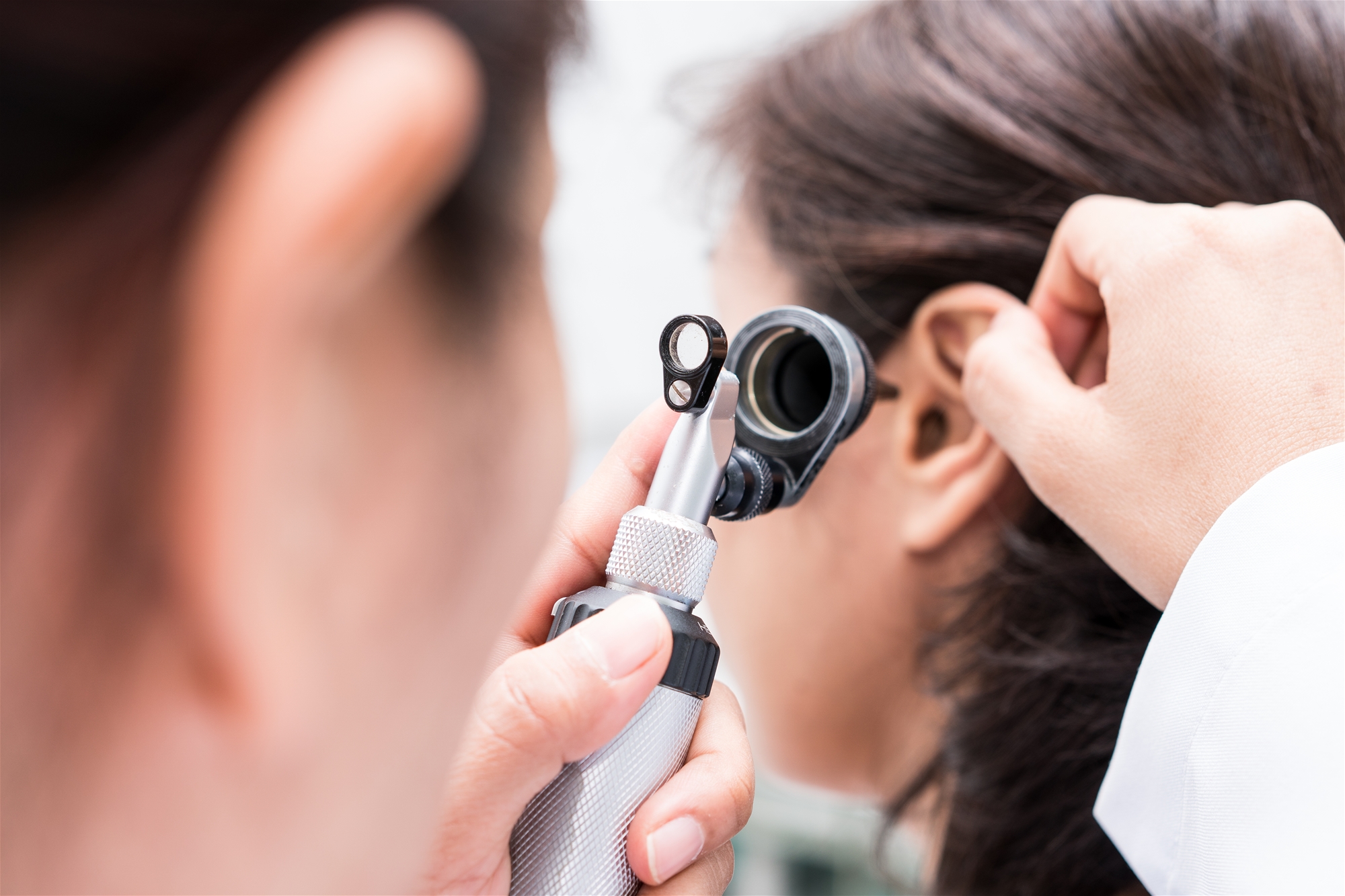
Diagnosis
- Otoscopy: The doctor examines the ear with an otoscope to see if the eardrum is reddened or purulent.
- Ear secretion culture: When there are purulent exudates, secretion culture is conducted to detect pathogenic bacteria.
- Tympanogram: Used to measure the pressure of the middle ear and the vibration of the tympanic membrane.
Treatment
- Treatment of pain: Take analgesics to relieve earache. The commonly used drugs are ibuprofen, acetaminophen, or ear drops.
- Medical treatment: choose the right antibiotics to fight bacterial infections, clean the ear canal regularly, and remove granulation tissue.
- When the mucus accumulates in the middle ear for more than 3 months, to avoid hearing damage, a hearing test and a small tube is inserted into the ear drum to help maintain drainage when necessary.
Prevention
- Patients newly diagnosed with acute otitis media should be treated with adequate antibiotics until the symptoms subside.
- Control allergic rhinitis: alleviate inflammation of the nose in children.
- Environmental control can remove some risk factors to avoid infection in children.

