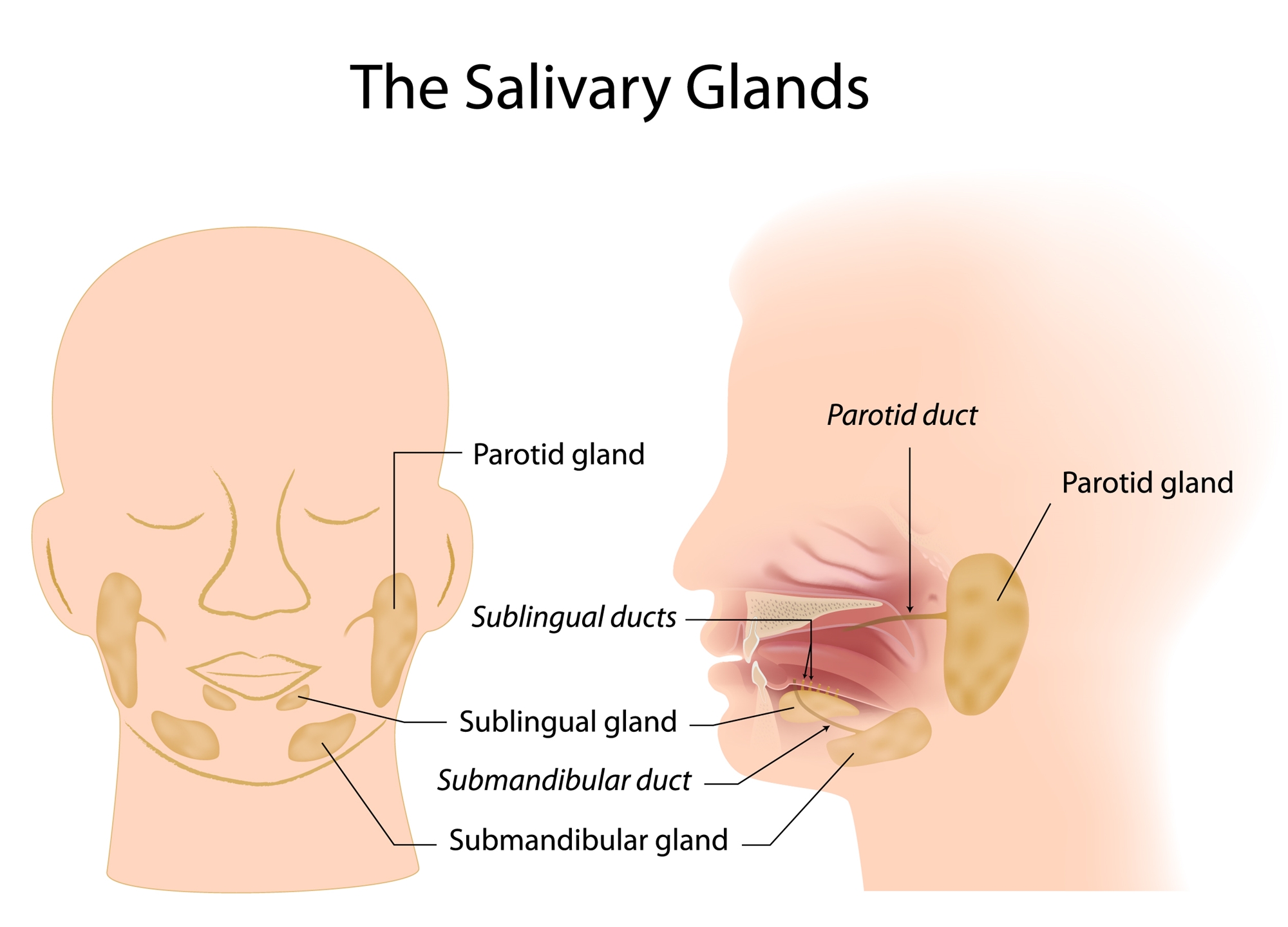
Inflammatory Salivary Gland Diseases
- Mumps: commonly known as “skin on pig head”(豬頭皮), is the most common inflammatory disease of the parotid gland, and the main symptoms are acute painful swelling of one or both parotid salivary glands.
- It only requires symptom treatment, with the disease cured in 5 to 7 days. It should be noted that mumps in children may be associated with aseptic meningitis, while mumps in adults may cause hearing impairment or orchitis, leading to the sequelae of male infertility. Some other diseases, similar to mumps in symptoms, such as neck lymphadenitis and purulent mumps, are caused by bacterial infections and need to be correctly diagnosed by doctors and treated with antibiotics.
- Acute suppurative parotitis: When squeezing the swelling parotid gland, if the purulent secretion can be found at the opening of the parotid duct in the mouth, the diagnosis will be confirmed. Oral or intravenous antibiotics are the main treatment.
- Sjogren's syndrome: A chronic, slowly progressing autoimmune disease. Typical clinical manifestations include dry corneal conjunctivitis of the eye and dry mouth.
- Examination methods of xerostomia include salivary flow measurement and salivary gland radiography. The biopsy of the lower lip salivary gland can confirm the diagnosis.
- In addition, xerostomia is also common in patients with head and neck cancer after radiotherapy, which mainly causes speech and eating problems. At present, besides water supplementation, only symptomatic treatment can be given.
- Sialolithiasis: Most of it occur in the submental gland, which may be caused by too little water intake or oral bacterial growth.
- Typical symptoms are slowly swollen jaws after every meal, especially when it's more acidic. If given local massage, swelling and pain will gradually subside.
- If the duct of the salivary glands is blocked by stones, the salivary gland is inflamed and painful due to arrested salivary secretion when eating. The treatment of submental gland calculi is to remove the calculi through oral incision of the submental gland duct.
Salivary Gland Tumors
- About 80% of salivary gland tumors occur in the parotid gland. Eighty percent of parotid tumors are benign, of which pleomorphic adenoma (also known as mixed tumors) is the most common, followed by Warthin's tumor. The latter seems to be increasing in recent years, which may be related to smoking. About 50% of submental gland tumors become malignant. Except for the common mucoceles, more than 80% of the tumors in the sublingual gland and salivary gland are malignant.
- To distinguish benign from malignant parotid tumors, fine needle aspiration cytology and imaging (computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging) are the main methods.
- Surgical excision is the main treatment principle for parotid tumors, whether benign or malignant.
- Submandibular gland tumors mostly manifest as painless masses in the submandibular region, while the most common clinical manifestations of sublingual and small salivary gland tumors are hard tumors in the oral cavity. Since the incidence of malignant tumors is often higher than that of parotid glands, surgical resection should be the main treatment principle.
- In addition, if salivary adenocarcinoma with high malignancy or cervical lymphatic metastasis is found in pathological reports after operation, additional radiotherapy is recommended to increase the local control rate. At present, there is not enough clinical evidence to support the efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy.

