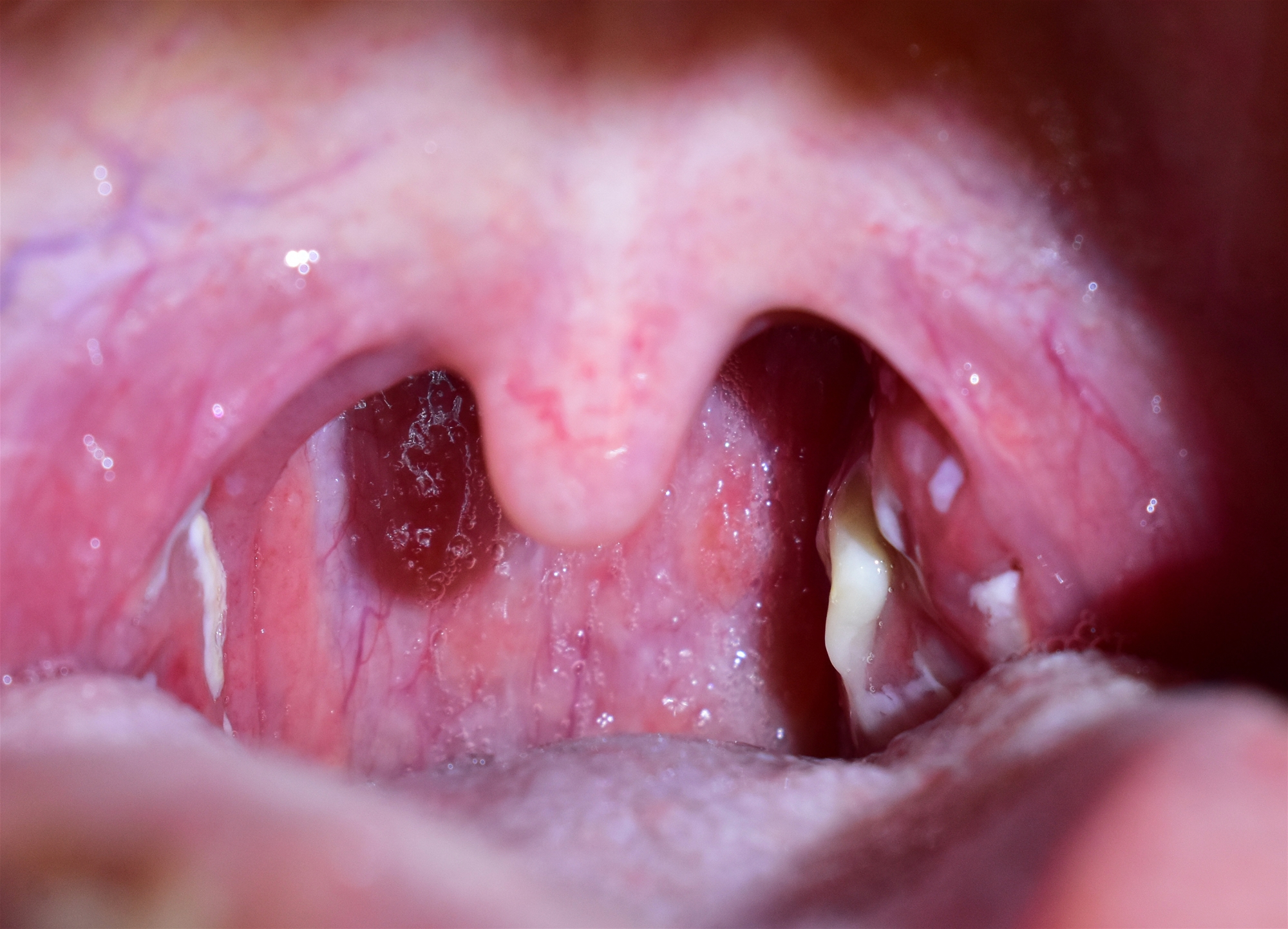
The tonsils are located at the back of the throat with two tonsil-like tissues on each side. The tonsils can be divided into three parts, the largest is the palatine tonsils, located on the velum, next to the uvula (the flesh in the middle of the throat), which is usually visible with the mouth open; the second is the adenoid at the deepest part of the nose, that is, the nasopharynx; and the third is the tonsil at the root of the tongue.
Tonsils have immune function and are the first-line defensive lymphatic system of the respiratory tract and digestive tract. They can react to many foreign invasive substances, such as viruses, bacteria, allergens, food, or environmental stimulants. Once there is inflammation, it is called tonsillitis. Tonsils often have irregular pits, forming a hotbed of pathogens, which can easily cause recurrent infections. Patients often mistake it for a cold and seek medical advice.
Symptoms
Tonsillitis is more common in preschool to mid-adolescent children. Possible symptoms include:
- The tonsils are red and swollen with white or yellow patches.
- Hoarseness, sore throat, difficulty swallowing and pain (children may not be able to accurately express their difficulty in swallowing in words, so parents can judge it from drooling and refusal to eat).
- Fever, swollen cervical lymph nodes, dyspnea.
- Stomach pain (especially in young children).
- Stiff neck, headache.
Causes
- Most tonsillitis is caused by a common cold virus, but other viruses or bacteria can also cause tonsillitis. Acute streptococcal pharyngitis can lead to rheumatic heart disease or nephritis.
Treatment Methods
- For bacterial tonsillitis, the doctor will prescribe an antibiotics treatment course, and patients must follow the doctor's instructions to go through the procedure. Viral tonsillitis cannot be treated with antibiotics, but medications can be administered to alleviate symptoms such as sore throat and fever. Proper home care is the focus, such as more rest, adequate water, gargling with saline, and avoiding contact with items that can cause throat irritation, such as tobacco and irritating food.
- Where severe tonsillar infections occur more than three times a year or more than five times in two years.
- Removal of the tonsils is recommended by the doctor when the tonsils are too large and are associated with sleep apnea (snoring) and serious complications, dysphagia, dyspnea, and other symptoms.
- In addition, the growth and degeneration of the tonsils should be symmetrical on both sides. If asymmetrical conditions are found, it may be tumors. It is also recommended that the tonsils be removed for pathological diagnosis.
If adenoids block the opening of the Eustachian tube, they are likely to cause middle ear effusion. If adenoids affect the drainage of the sinuses, they will cause chronic sinusitis. As a result, adenoidectomy is often performed in conjunction with the middle ear ventilation tube insertion in children, which has been shown in the literature to reduce the chance of middle ear effusion and sinusitis recurrence. Moreover, lingual tonsillitis is less likely to cause respiratory obstruction or swallowing problems, and removal of the lingual tonsils is not generally considered a routine procedure.
To remove tonsils, patients and family members often have doubts about whether their immunocompetence will be undermined. As a matter of fact, after adolescence, the immune activity of the tonsils decreases gradually, and the defensive function is replaced by other lymphatic systems. Therefore, the removal of the tonsils in adults will not have any side effects of immunodeficiency. Even though the tonsils of children still have immune function, the other lymphatic systems of the body also have defensive effect, so they are not "unarmed" against external pathogens.
Statistically, patients who had their tonsils removed as children do not have lower levels of immunoglobulin in their blood as adults, meaning their immune function is not compromised.
Prevention
Good hygiene is the way to avoid infection. It is advised to wash hands frequently, especially after going to the toilet and before eating, and avoid sharing food
Reminders
After tonsillectomy, about two to three weeks, both adults and children should avoid lifting heavy objects, eating irritating food (e.g. chili and alcohol) and excessive throat exertion to reduce the risk of postoperative bleeding.

