About the prostate
The prostate is a male organ, located under the bladder, about the size of table tennis. Its main function is to secrete the prostate fluid and maintain sperm motility after ejaculation.
Prostate cancer
Nowadays, prostate cancer has surpassed bladder and kidney cancer in urinary tumors to become the most common malignancy of urinary system, and the mortality rate is still on the rise. In 1971, the mortality rate per 100,000 people was 1.2, and in 2002, it had risen to 6.5, ranking eighth in cancer deaths in that year.
The incidence of prostate cancer is related to age, family history, ethnicity, and dietary habits. In recent years, due to the westernization of living and eating habits, the incidence of prostate cancer has risen rapidly. It is generally believed that high animal fat content in the diet will increase the risk of prostate cancer.
Early prostate cancer is mostly asymptomatic, and the presence of symptoms often means local invasion or metastasis. Dysuria, frequent urination, hemospermia, even bone pain, lower extremity lymphedema, or hydronephrosis usually indicate a more advanced course of the disease.
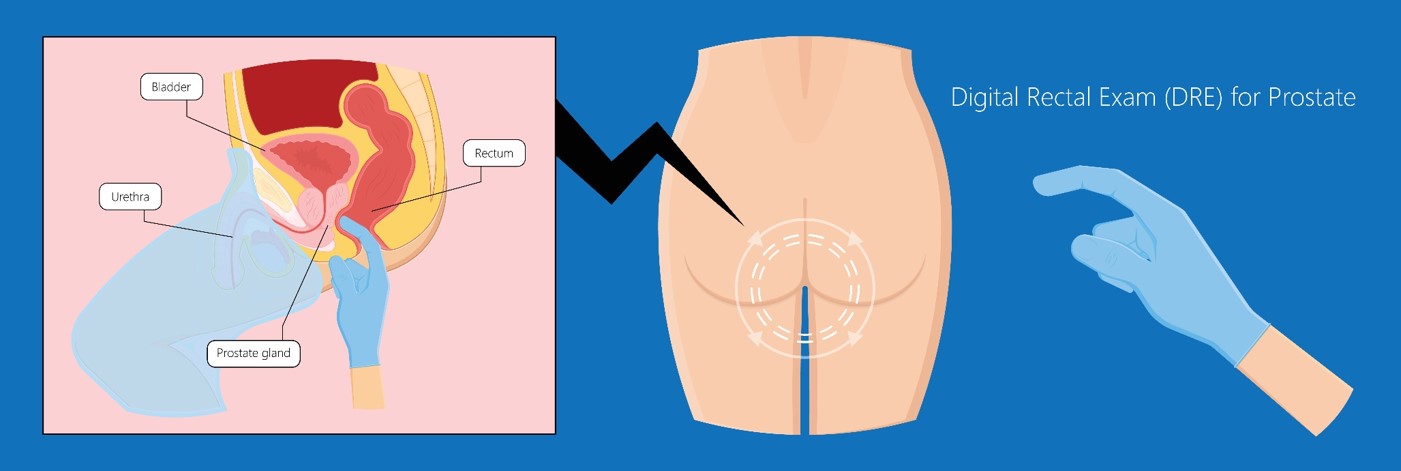
Digital rectal exam
At urological clinics, the most direct and effective screening for the prostate gland health is a digital rectal exam, which is another screening method in addition to prostate-specific antigen (PSA) for early detection of prostate cancer. Reach into the anus with a finger about 4cm deep, where if a lump is felt, it may be cancerous, but the drawback is that you cannot feel its existence if too small.
During a digital rectal exam, the patient is first asked to lie on his side on the examination bed. After communicating with the patient, the doctor will put on gloves, apply lubricant, extend a finger into the rectum through the anus, and examine the prostate gland and seminal vesicle in front of the rectum, which usually takes about 10 seconds. During the process, the physician first examines the strength of the sphincter contraction to determine whether the patient has a neurological or functional problem, then presses on the prostate gland to assess the size, presence of any lumps or even significant cases of heat and tenderness, and finally checks the rectal wall in a circular motion for lumps or fistula.
In the process of examination, it will bring some discomfort to the patient, such as swelling pain and urinary urgency, etc., but the doctor can directly assess the size of the prostate gland and whether there are suspicious lumps in the prostate or rectum in the shortest time.
A digital rectal exam is a procedure that can provide a lot of information about diagnosis and treatment quickly. It is still an important screening tool in the physical examination by urologists, even with the great progress in medical imaging technology and tumor markers. Therefore, we suggest that you consult with your attending physician to assess whether to receive this test based on his/her professional judgment after full discussion.

