Medications used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
The conventional medications used for rheumatoid arthritis include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). With the rapid development of biological agents in recent 20 years, the treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis are more diversified and the therapeutic effect is greatly improved.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
They have analgesic and antipyretic effect, but will not change the course of the disease. Conventional anti-inflammatory drugs (non-selective COX-2 inhibitors) have more side effects, and a new generation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (selective COX-2 inhibitors) with fewer side effects have been developed.
- Corticosteroids
can effectively reduce the symptoms of joint inflammation, but long-term use of high doses of steroids is more likely to cause side effects (e.g. moon face) and sequelae (e.g. osteoporosis, cardiovascular risk), so it is advised to use low doses of steroids.
- Conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs)
can delay the course of the disease and prevent the immune system from further damaging the organs, take a longer time to take effect, and the tolerance of long-term use is not good, and the occurrence of side effects should be paid attention to.
- Biological agents (bDMARDs) and small molecule inhibitors
They can inhibit specific targets in the immune mechanism of rheumatoid arthritis. Biological agents can not only relieve symptoms more quickly, but also have less side effects. Because of its high cost, biologics are currently only approved in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who have failed to respond to DMARDs treatment.
At present, the biologic agents covered by the National Health Insurance program can be divided into the following types according to different objectives:
- Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, including " Enbrel," "Humira," "Simponi" and "Cimzia": are the first-line drugs in biological agents (other types of biological agents can be used only when these drugs are ineffective).
- B-cell targeted therapy with Mabthera (rituximab): the second line drug in biological agents in Taiwan.
- T-cell targeted therapy with Orencia (abatacept): the first line drug in biological agents.
- IL-6 targeted therapy with Actemra (tocilizumab): the first line drug in biological agents.
In addition to biological agents available for use, National Health Insurance currently also provides small-molecule inhibitors (targeted synthetic DMARDs), including "Tofacitinib" and "Baricitinib" : both oral drugs (with the same efficacy as biological agents).
How to evaluate the therapeutic response?
RA patients expect their joint symptoms to disappear completely after treatment. But many patients who have this disease for many years find it difficult to achieve good therapeutic effects (in disease remission). At this point, doctors have to settle for second treatment goal: Treatment that reduces the activity of the disease can also go a long way in making the patient feel better (in low disease activity). So it is important to calculate the "disease activity" of rheumatoid arthritis in the evaluation of therapeutic response.
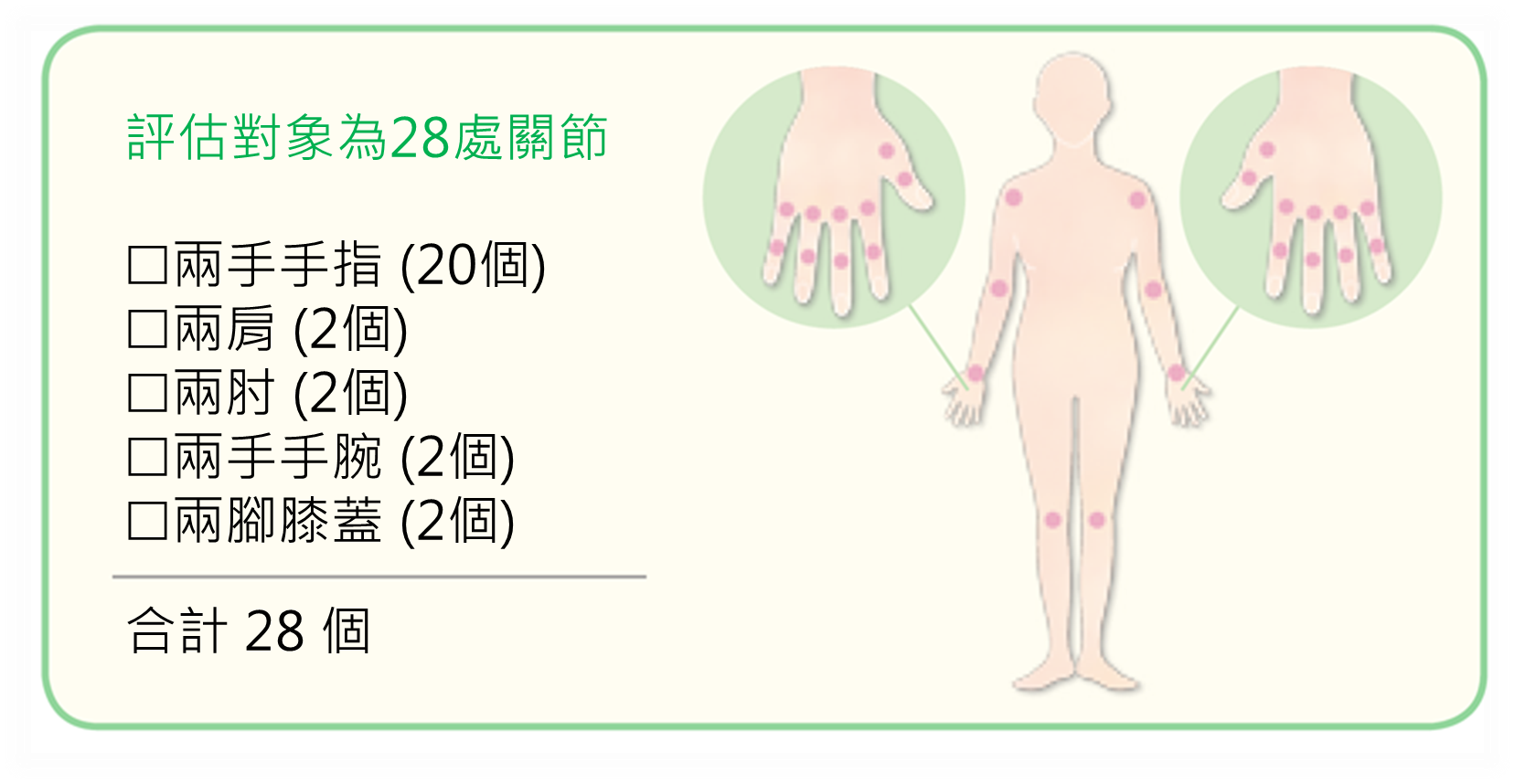
The Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28) is the most commonly used tool to evaluate the disease activity of patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Taiwan. It can be used to evaluate the therapeutic response of medication by the number of tender or swollen joints in 28 joints, the sedimentation rate of red blood cells and the overall health status of patients.
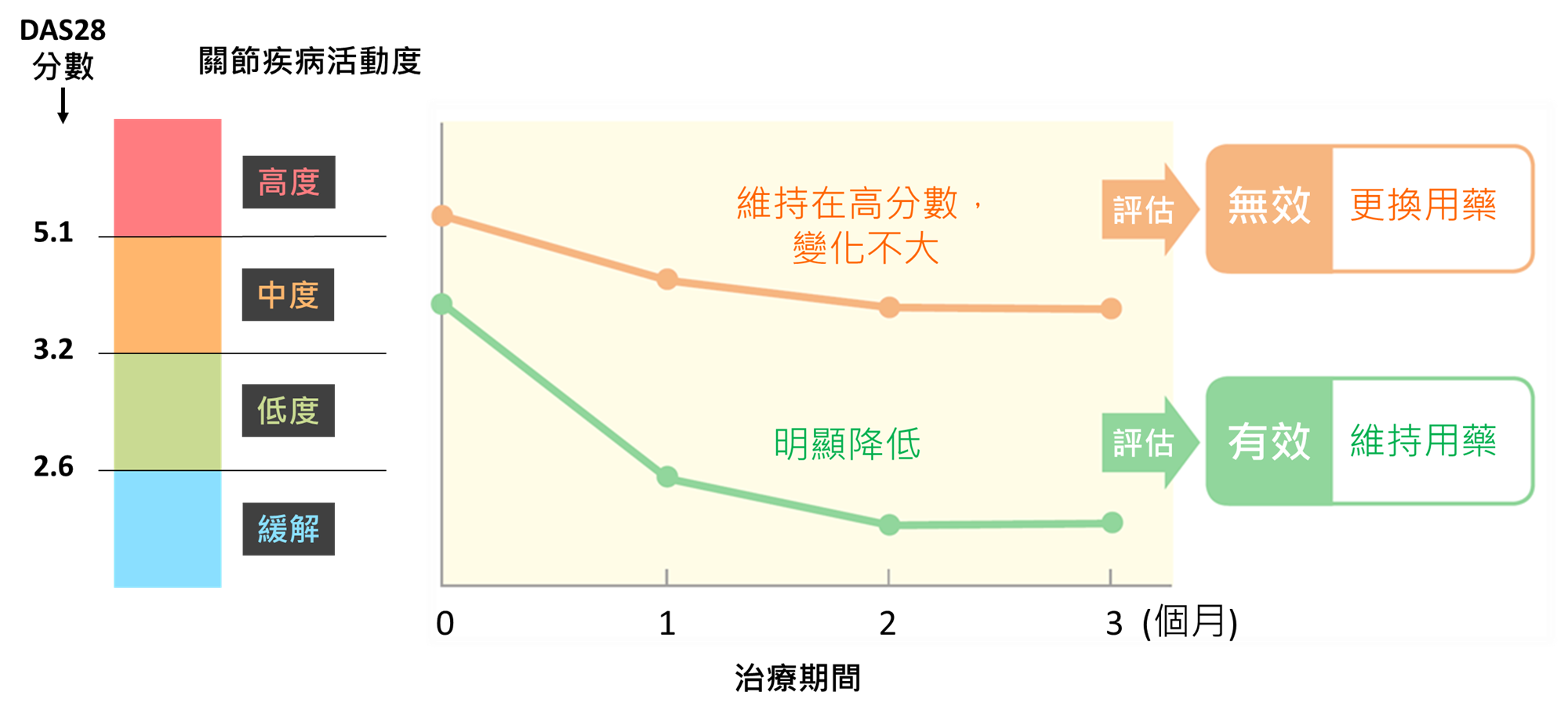
The DAS28 represents a specific number of degrees of disease activity. DAS28 < 2.6 is the ultimate therapeutic goal (treat-to-target) of rheumatoid arthritis - "complete remission"; DAS28 between 2.6 and 3.2 is the next best alternative treatment target, "low disease activity." Comparing the DAS28 values before and after treatment allows the physician to objectively assess whether the treatment has achieved the desired goal, and to decide with the patient whether to adjust the treatment direction.
- DAS28 calculation method
❶ Assessment of joint damage by physician
Palpation is used to assess the number of tender and swollen joints in the patient's 28 joints.
❷ It's up to the patient to assess their overall health
Using a 100 mm scale provided by the physician, patients can choose a mark from 0 to 100 that best fits their overall health status.
❸ Blood test in hospital
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of the patient is measured by blood tests, which represents the degree of inflammation in the patient.
The DAS28 can be calculated after the results of ❶, ❷ and ❸, are brought into a specific formula.
Daily care
Proper exercise and rest
- Continuous and regular exercise is important to maintain joint mobility and muscle power.
- Proper exercise can help maintain weight, ease joint strain, and reduce bone loss.
- Exercise that places too much strain on the joints should be avoided, but swimming is a good option and can work without putting too much pressure on the joints.
- If the joint is inflamed, do not engage in strenuous exercise to avoid aggravating the inflammation symptoms.
- Adequate sleep and rest are also important for the care of damaged joints.
Proper cold / hot compress
- Cold compresses can temporarily relieve joint pain after exercise or when symptoms are acute.
- In less severe cases, hot compresses can help relax the muscles.
- Patients with hypersensitive skin or poor blood circulation may not be suitable for cold and hot compresses.
A balanced diet
- Like exercise, a balanced diet with regular and fixed amounts for three meals can help maintain weight, meet nutritional needs and reduce the burden on joints.
- The Mediterranean diet is also thought to help fight inflammation, which can be alleviated by deep-sea fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Dietician recommends reducing the intake of sugar and animal fats to lessen the chance of obesity or atherosclerosis.
- Foods rich in vitamin D and calcium can reduce bone loss.

