Why is this so important?
Tripping on your toes is one of the common causes of morbidity and leading causes for nonfatal injuries; and sometimes it causes severe health problems such as fracture, hemorrhage, and even death. Older adults often have higher risk of falling for they often suffer from age-related changes like unsteady gait, reduced vision like presbyopia, health-related fragility, and stiff joints. These causes often affect your health and require your attention to prevent them.
Who might be at increased risk for falls during their hospitalization?
- People over age sixty-five.
- People with falling history.
- People suffering from bewilderedness, disorientation, and drowsiness.
- People with ill vision or loss of sight.
- People suffering from headache, dizziness, and hypotension.
- People with unsteady gait and weakness in lower limbs should use assistive walking aids.
- People in need of assistance for bathroom use.
- People on medications like sedative tranquilizers, pain killers, diuretics, antihistamine, antidiabetics, chemical therapy, and anti-hypertension.
How can we prevent falls in the hospital?
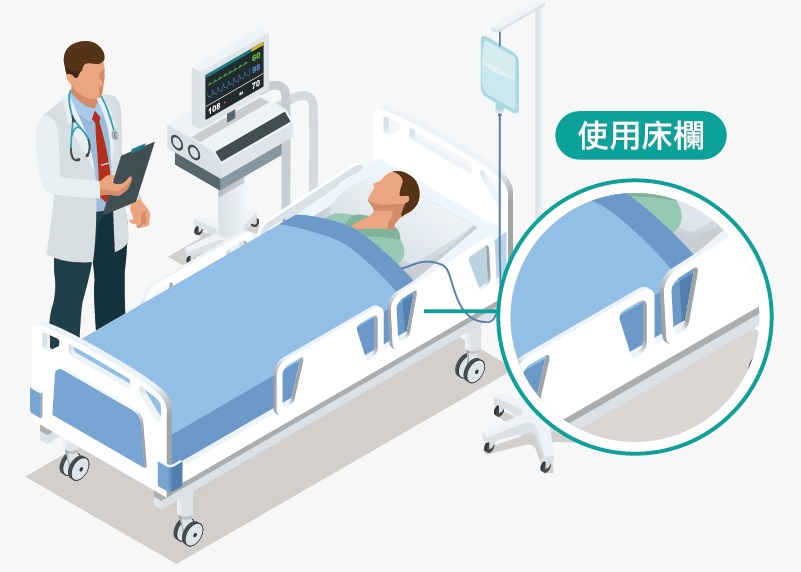
- Use bed railings
When you suffer from disorientation, confusion, dizziness, and headache; ask for assistance from our medical staff.
- Put down your side railings before getting up from a lying position, and do not climb over the side railings. When you need help, please feel free to call your healthcare providers for help.
- You can prevent a fall by using your side rail when you are asleep.
- If you feel any dizziness, vision problem, weakness, or any other health problems during hospitalization, please inform your healthcare providers.
- Get out of bed
- Please ask your health care providers to check on your blood pressure in two different positions: one you’re your lying position and the other with standing position. Ask for help when you need to change positions.
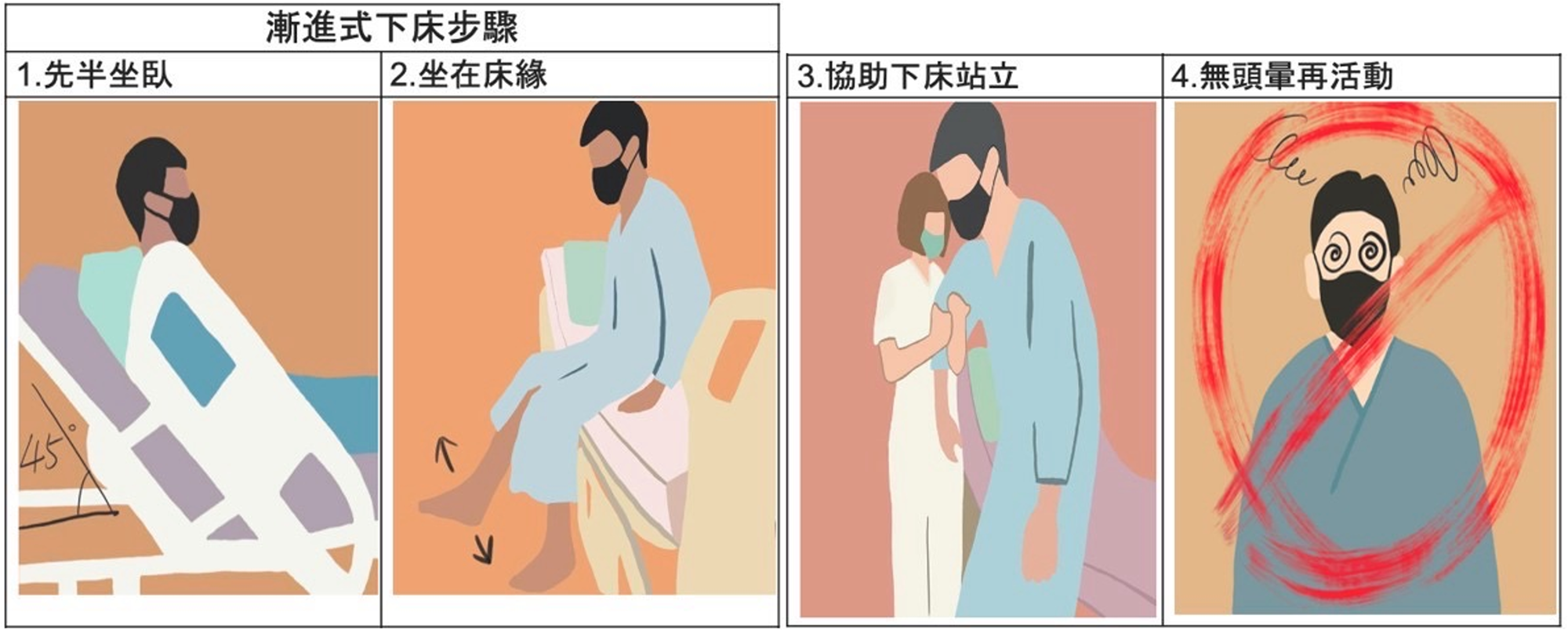
- Ask your doctor or nurses about the medications you are taking because some medications like anti-hypertension and sleeping pills may cause dizziness and weakness. Ask your caregiver to help you get up from a lying position slowly. Firstly, you lie on the bed with your head raising 45℃, and then sit on the bed for 5 minutes. Secondly, sit on the bedside and move your feet for 5 minutes to increase you muscle strength, and then try to stand on the floor and walk around.
- If you have unsteady gait, do not get out of bed by yourself, and always use assistance devices like wheelchairs, walkers, and canes, or request assistance from our medical staff.
- Walking
- Use walkers or cans within your reaching distance to help you stabilize gait
- Wear appropriate clothing and sturdy, stable, non-slip shoes of appropriate size. Do not go barefoot.
- Keep the toilet floor dry. Inform our staff if you notice any water on the floor; make sure that there is no obstruction in the aisles and maintain the brightness of the room.
- Be aware of the bathroom risks
- Avoid wet floor in and out of the bathroom to prevent slipping on your feet.
- Ask your caregiver to stay with you when you use the bathroom.
- Turn on the light and keep the bathroom lighted when it is dark.
- Change your position slowly when you are in the bathroom.
- Use electric call bell in the bathroom if you need help.
- Use the bathroom before taking medications such as sedatives and tranquilizers or painkillers. After taking the medications, bed rest for an hour to prevent tripping caused by dizziness.
- If you feel weak after taking medications, please use pot or bedpan.



